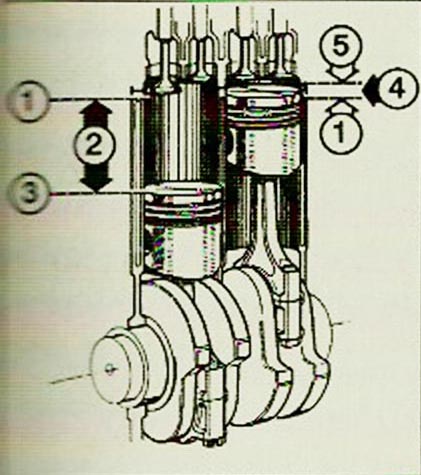
 Displacement – (2) covers the cylinder space between TDC (1) a DMP (3) plunger. Combustion chamber (4) is the space between the recess in the cylinder head (5), with the piston crown in TDC position (see plunger on the right)
Displacement – (2) covers the cylinder space between TDC (1) a DMP (3) plunger. Combustion chamber (4) is the space between the recess in the cylinder head (5), with the piston crown in TDC position (see plunger on the right)
Four-stroke engine. The piston makes four strokes in one cycle.
Inlet (water 1.). Piston moves down to bottom dead center (DMP). The intake valve opens. The fuel-air mixture in a gasoline engine enters the cylinder.
Compressing (water 2.). The piston moves from bottom dead center (DMP) towards top dead center (GMP). When the inlet valve is closed, the piston compresses the mixture.
work (water 3.). Shortly before TDC, a spark jumps between the spark plug electrodes. The mixture burns, and the increasing gas pressure moves the piston towards the BDC. The cord shaft rotates through the connecting rod.
Departure (water 4.). the piston moves up again. The exhaust valve opens and exhaust gas flows into the exhaust system.
Displacement. This is the space inside the cylinder, measured from BDC to TDC position of all pistons. There is still space above the piston in its TDC, called the combustion chamber, in which there is a fuel-air mixture. Together, the cylinder displacement and the combustion chamber form the total cylinder displacement.
Compression ratio. It is the ratio of the cylinder capacity to the combustion chamber capacity. It determines the volume to which the fuel-air mixture is compressed in relation to the cylinder capacity. The compression ratio of gasoline engines is approx 10, and diesel engines approx 20.
