Compression pressure measurement – Golf 4 , Bora.
Next steps:
1. Warm up the engine before starting measurements. The oil temperature should be at least 30 ° C (the oil filter noticeably warm). With warm oil, the piston rings seal better. However, the engine temperature must not be too high, because when unscrewing the spark plugs you can damage their threaded seats in the head. Remove the engine cover.
Gas engines
2-4 Disconnect the electrical power to the ignition system, remove the ignition coils and remove all spark plugs. Remove the fuel pump fuse and pull out the plugs of the electrical connectors of the injectors.
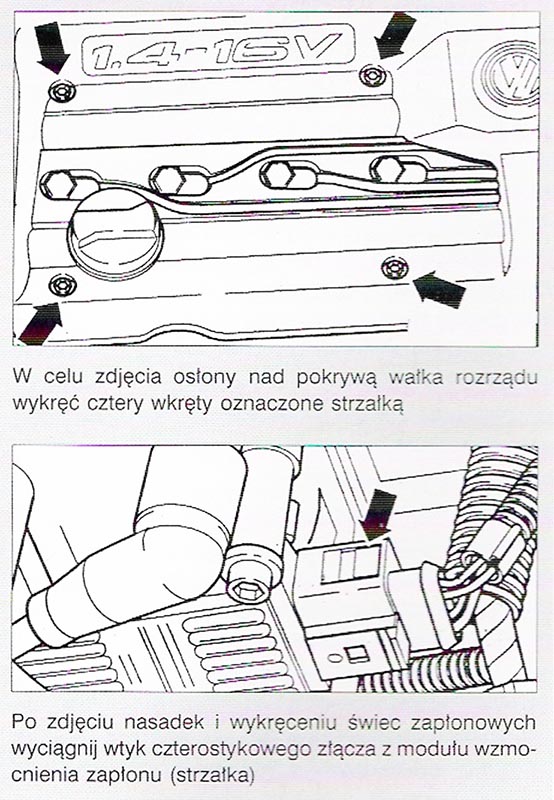
AHW motors, AKQ, APE/AXP, ATN/OFF: remove the cover over the camshaft cover and disconnect the high-voltage wires and spark plug caps. Remove the candles. Pull the four-pin connector out of the ignition amplification module.
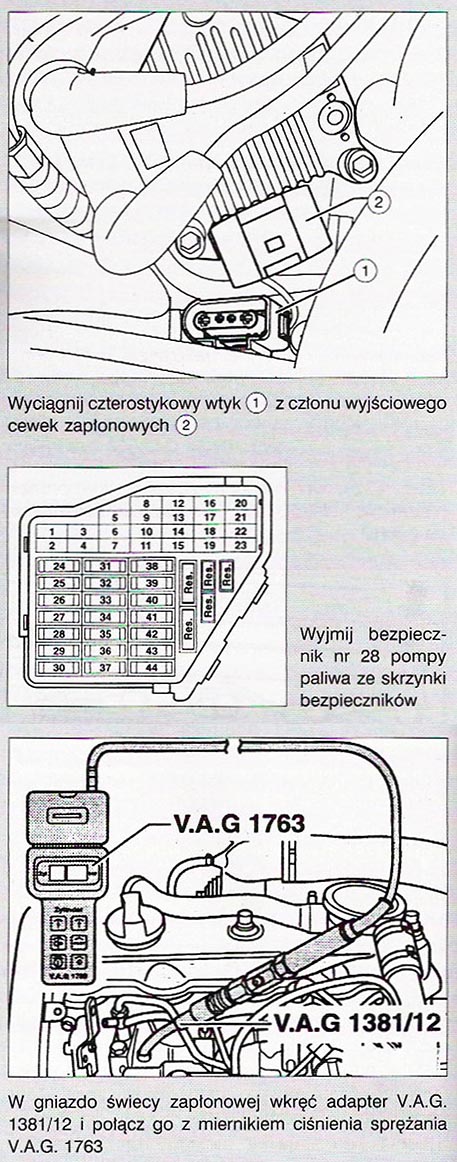
AEH motors, AKL, APF: pull out the four-pin connector (1) from the output stage of the ignition coils (2). Remove fuse no 28 the fuel pump and remove the plugs of the electrical connectors of the injectors. Remove the spark plug caps 1. i 4. cylinder with tool T10029, and candles 2. i 3. cylinder with the V.A.G.. 1922. For APK and AQY engines, all spark plug caps can be removed with the T10029 tool. Remove all spark plugs.
AGN motors, AGU, AQA and ARZ: remove the fuse no 32, thus breaking the power supply to the injectors. Remove the engine cover. Remove the electrical connector plugs from the ignition coils. On vehicles with a turbocharger, it is necessary to remove the ignition coils. On an AGN engine, remove the caps from all spark plugs.
Diesel engines
2 In SDI engines (AGP, AQM) remove the top of the intake manifold. On SDI and TDI engines (AGR, ALH. AHF) remove the connector plug from the fuel shut-off valve on the injection pump and the connector plug from the fuel dose regulator of the injection pump.
3 Remove all glow plugs with a V.A.G key. 3220.
4 Screw the V.A.G adapter into the spark plug socket. 1381/12 and prepare the V.A.G.. 1763 to carry out the measurements.
All engines
5 Apply the emergency brake and put the gearshift lever in neutral.
6 Have your attendant turn on the pacemaker for about five seconds (eight revolutions of the shaft), that is, until the indicator of the pressure tester stops. Reactivating the starter with the accelerator pedal fully depressed will fill the cylinders to the maximum. attention! Do not lean over the engine while the starter is operating, so that the soot particles from the cylinder do not hit you in the face.
7 Read and write down the measurement result. Using a graphical instrument and measurement card, go to checking the next cylinder.
8 The tester must be vented after each measurement.
9 On gasoline engines, re-insert the plugs into the connector sockets on the injectors and the output member of the ignition coils (if it is in your engine) and tighten the spark plugs with a torque wrench.
10 On diesel engines, the glow plugs must be tightened to the torque level 15 Nm. Connect the wires and insert the plug into the socket of the fuel shut-off valve on the injection pump.
The rubber end of the compression pressure tester must be tight against the spark plug socket hole (in a glow plug diesel engine). A helping person, at your signal, he turns on the starter, which must work until the moment, in which the instrument pointer will no longer deflect.
Measure the compression pressure on all cylinders sequentially. More important than the pressure itself are the differences in its values in individual cylinders.
11 On all engines, disconnecting the connector in the injection system will record the fault in the memory of the electronic engine control unit. Such a record can be deleted from the diagnostic memory of the control device at an authorized VW workshop.
If compression pressure is showing symptoms (noise, blowing, sediments etc.) in one of the places mentioned, the reasons for this may be as follows:
■ intake manifold or suction silencer: damaged intake valve,
■ open radiator or coolant expansion tank: damaged head gasket or broken head,
■ open oil filler neck or dipstick: worn cylinder walls, piston skirt (lateral surface) or piston rings,
■ blowing noise in the muffler: leaky outlet valve.
